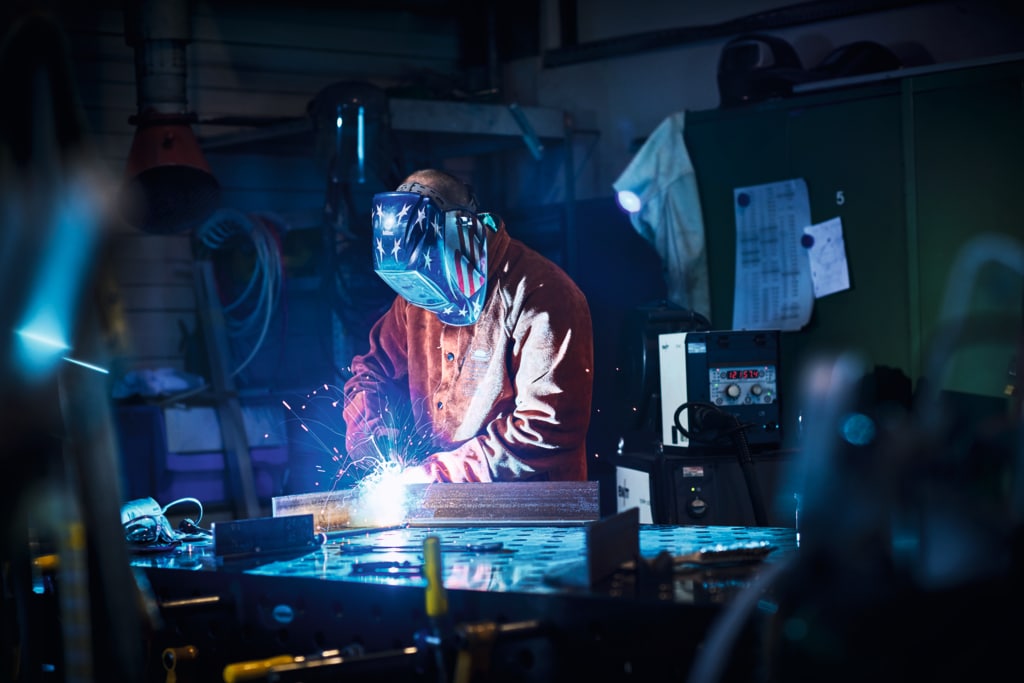
The SMB friendly safety stack (mapped to the welding workflow)

Goal: Follow the hierarchy of controls—substitution → engineering → admin → PPE—to reduce exposure at each step of the weld cell.
1: Before the arc: choose safer inputs
- Low manganese filler metals: Lower Mn content helps reduce a key neurotoxic exposure driver in the fume mix. Pair with good process control; still verify with air monitoring.
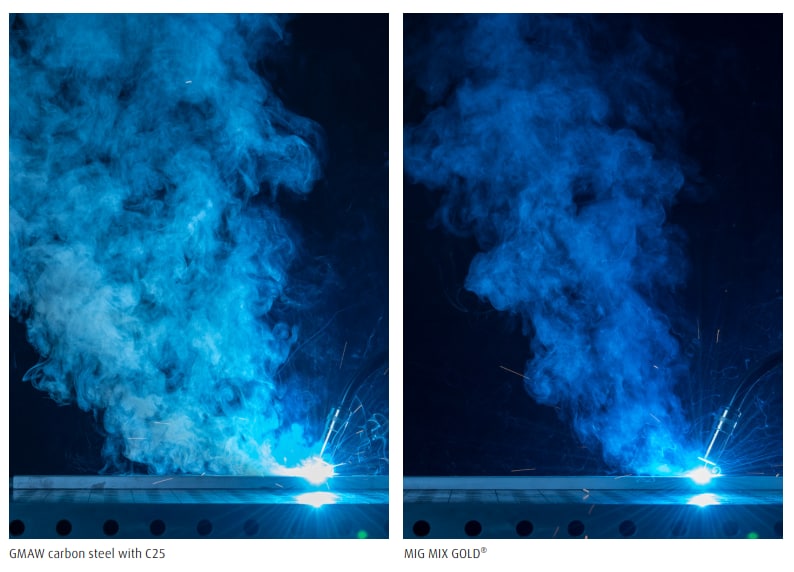
- MIG Mix Gold (shielding gas blend): Optimize the gas for stable arc, low spatter, and consistent puddle control, helping reduce rework and post weld abrasion needs. (mixture specifics vary; implement per WPS and qualify.)
- Welding chemicals (e.g., Whale Spray): Use purpose built anti spatter/cleaners to minimize grinding and airborne fine particulates downstream; ensure SDS alignment and proper ventilation.
2: At the arc: remove fumes where they form
- At source capture MIG guns: Integrated extraction captures a high percentage of fume directly at the nozzle without compromising shielding gas when properly configured; boosts welder mobility vs. fixed arms.
- Independent studies show on torch extraction reduces nanoparticle exposure in the welder’s breathing zone during arc welding.
3: Around the arc: contain and protect
- Welding screens, custom screens & curtains: Control line of sight light/radiation, define safe zones, and help manage bystander exposure while supporting airflow design per CSA guidance.
- Abrasives (pre/post weld): Choose high efficiency abrasives that cut faster and cooler to minimize airborne dust load and time at risk. Pair with downdraft or on tool extraction where feasible (see automation below).
- PAPR welding helmets:
- Provide clean, filtered air and increased comfort during welding and grinding tasks.
- Different models offer varying levels of protection — choose systems tested and validated by the manufacturer and ensure they’re used under a compliant safety program.
- PROSTAR PPE: